Customer segmentation isn’t just a buzzword in today’s eCommerce landscape; it’s a crucial cornerstone of any strategic marketing plan.
Your target customers have unique needs, traits, and pain points, and one key for effective marketing is identifying the needs of each group, to provide them with the messaging most relevant to them.
Segmentation helps you group shoppers that share similar characteristics to better satisfy the needs of each group.
Customer segmentation enables brands to:
- Target customers better
- Optimize the customer journey to ensure continuity
- Develop productive marketing strategies
- Increase customer acquisition and retention
And so much more. But customer segmentation will only be effective if your strategy is actionable.
Leverage customer segmentation by understanding what it is, why it is important for eCommerce, how to develop effective customer segments, and the effect it has on eCommerce growth.
What is Customer Segmentation: A Brief Refresher
7 Benefits of Customer Segmentation
3 Segmentation Models for eCommerce
How to Develop & Convert Effective Customer Segments
What is Customer Segmentation: A Brief Refresher
Customer segmentation, also known as marketing segmentation, is the process of dividing customers into subgroups that share similar characteristics and variables including demographics, interests, and behavior.
Segmentation creates smaller, specific groups of customers for brands to more effectively acquire and retain their target buyers.
7 Benefits of Customer Segmentation
You can’t succeed in eCommerce — or business — without segmentation.
The reason most online retail brands engage in customer segmentation boils down to driving eCommerce profits via sustainable and effective digital marketing.
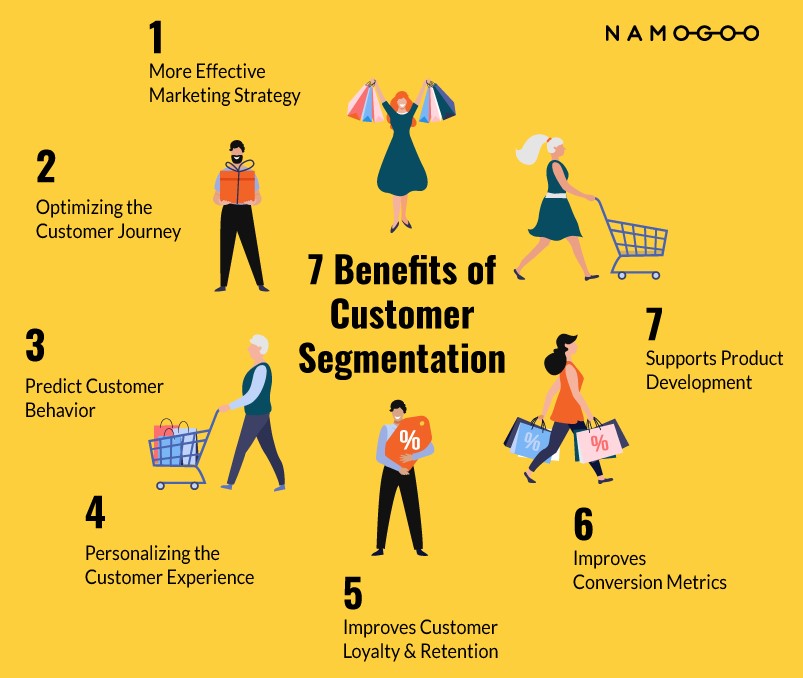
Customer segmentation helps you to achieve that by unlocking the benefits below.
#1. Improved eCommerce Marketing Strategy & Profitability
Customer segmentation allows for a deeper understanding of the customer so you can:
- Prioritize acquisition channels and market to your target audience on the channels they’re most likely to engage with
- Be more precise with your targeting of your suspects, prospects, leads, and customers, serving them with specific messaging and creative.
When you know where to find your target customers and how to engage them, you benefit from a more effective, profitable marketing strategy.
Customer segmentation also helps you to prioritize your team’s marketing budget and resource allocation to focus on the channels, customers, and prospects with the strongest return on investment.
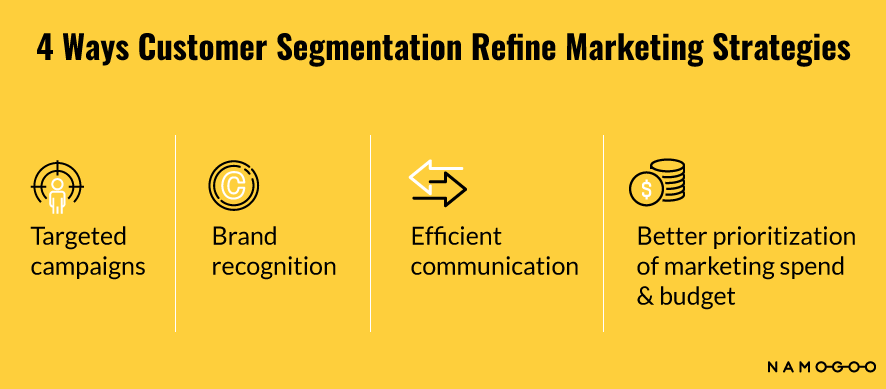
Check out the ways customer segmentation helps to refine your marketing strategy. It triggers:
- Targeted campaigns: Identify a more precise audience for your campaign, fine-tune a stronger marketing message, and serve it to the relevant consumers.
- Brand recognition: A more specific message makes your brand stand out. People will remember your products based on their value propositions that meet their needs.
- Efficient communication: Knowing your customers helps marketing teams to connect with them on the right channel. It can be on social media, email, events, content marketing, and more.
- Better prioritization of marketing spend & budget: Choosing specific channels, customers, and prospects with the strongest return on investment can help you reduce CAC and more efficiently allocate your budget.
#2. Provides Insights to Optimize the Customer Journey
Customer segmentation can help you understand what might motivate each group to move from the awareness stage to the consideration stage, and then to the conversion stage and beyond.
When you know your customers, you can meet their needs more easily, and you can optimize the customer journey stages to ensure journey continuity.
#3. Predicts Customer Behavior
The ability to predict future customer behavior is a benefit of segmentation.
This allows you to understand the shopper’s intent, to meet current needs and assess future actions.
If you can predict a customer’s future behaviors and engagements with your brand, you can get in front of them at each stage of their customer journey to:
- Remove barriers to journey continuity
- Provide relevant promotion
- Offering the right messaging at the right time.
This helps you move customers toward the conversion stage faster, and improve customer lifetime value (LTV) as you personalize the customer journey and experience in alignment with your predictions.
#4. Enables a More Personalized Customer Experience
Online shoppers expect personalization in today’s eCommerce landscape, not only to convert but to be retained.
44% of consumers become repeat customers after a personalized shopping experience[*], and customer segmentation enables a more personalization that goes beyond generic interactions.
While onsite and marketing personalization can get incredibly savvy with AI-driven predictive analytics and machine learning tools that outpace customer segmentation’s capabilities, segmentation often bridges the gap between a generic customer experience and one with a degree of personalization.
#5. Improved Customer Loyalty & Retention
Customer segmentation allows you to identify your most valuable customers, and develop programs, content, and incentives to reward them and keep them happy and engaged.
It allows you to differentiate between first-time, repeat, and loyal customers and tailor your brand’s efforts and communication to each group, providing the incentives, marketing campaigns, and messaging they need to repurchase.
Customer segmentation can help you understand the key behaviors that lead to brand loyalty so you can optimize the customer journey and marketing funnel to surprise and delight existing customers and win their support.
It can also help to identify those customers who are most likely to churn or become lapsed customers, and provide them with resources to keep and take them back to the purchase stage.
#6. Improved eCommerce Conversion Metrics
Importantly, customer segmentation drives revenue and bolsters all related conversion metrics, including:
- Conversion rate: Segmentation enables conversion rate optimization through onsite personalization, a stronger sales promotion strategy, and customer journey continuity.
- Average order value and cart size: Because you can understand which customers are most likely to be up- or cross-sold, try new products, and appreciate add-ons — and which products to offer.
- Abandoned cart rate: Segmentation helps you identify the customers who have abandoned their cart, and remind them to check out or incentivize the purchase.
These all help to drive more revenue, which you can then reinvest back into growth.
#7. Supports Product Development
Insights from data can be used to discover product development opportunities or trends for your buying team, helping to shorten the validation and market testing phase.
A data-driven customer segmentation strategy helps your team to develop products your customers will love without having to allocate time and resources to focus groups or risk making a purchase order for a product that will flop.
Consumers tend to change their habits, preferences, and priorities so they don’t always stay in the same group. Use customer segmentation to make sure you have updated information about your target audience and even find untapped channels and opportunities.
Now that you know the main benefits of customer segmentation, it’s time to dive deeper into the models of segmentation.
3 Segmentation Models for eCommerce
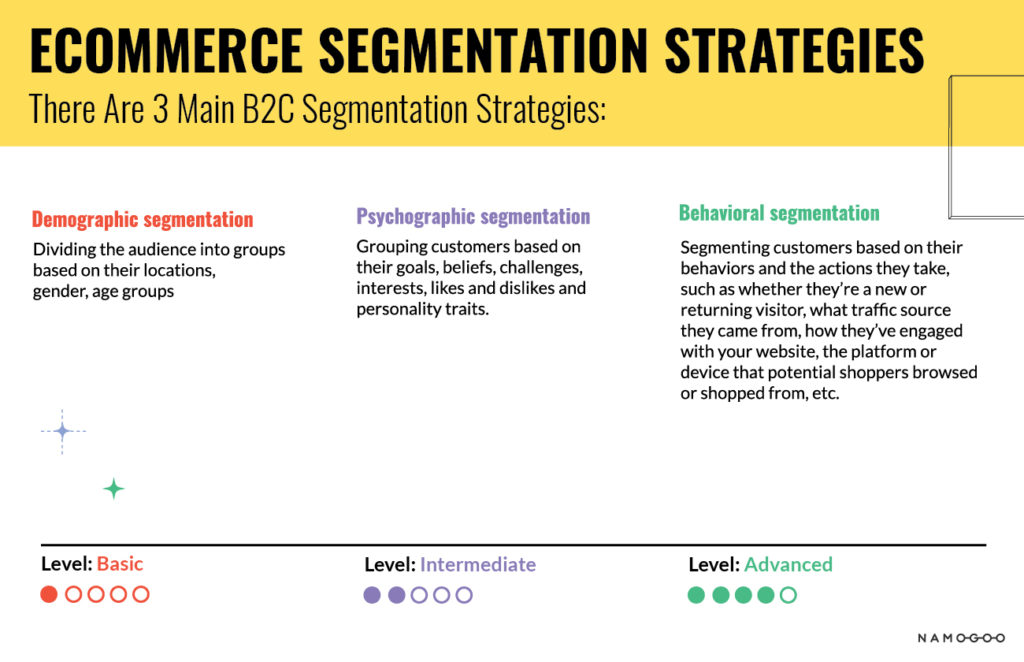
There are three main segmentation models used in eCommerce and B2C companies:
- Demographic segmentation: Dividing the audience into groups based on their location, gender, age group, etc.
- Psychographic segmentation: Grouping customers based on their goals, beliefs, challenges, interests, likes, dislikes, and personality traits.
- Behavioral segmentation: Segmenting customers based on their behaviors and the actions they take, such as whether they’re a new or returning visitor, what traffic source they came from, how they’ve engaged with your website, and the platform or device they’re using.
To make each customer segmentation method more effective, it is best supported with other types of segmentation. Here are the basics of these strategies:
Demographic Segmentation
When people think of segmentation, demographic segmentation tends to be the most common model that comes to mind. It is the easiest data to gather and is widely used to create customer subgroups.
Here are the types of demographic segmentation:
- Age: Basic factor to look at for a customer and continuously change. The categorization can range on specific life cycles from children to seniors or generation-based like millennials, gen X, gen Z, etc since these groups grew up with slightly similar experiences.
- Gender: When grouping customers based on gender, be careful on stereotypes including colors like blue = masculine.
- Geographic location: The country, state or province, region, or city they live in.
- Occupation: This includes income targeting such as measuring your customers’ buying power and occupation targeting which looks into the industry a customer is in.
- Income: A measurement of the customer’s buying power based on their household or individual income brackets.
- Education: What level of education the customer has achieved
- Ethnicity/Religion: This is an essential grouping since individuals may have conflicting interests, preferences, and beliefs.
This segmentation model is basic and easily executed. It is used in B2B and B2C companies.
Demographic Segmentation Example
Namogoo customer Upwork may create a segment based on demographics to target small business owners (occupation) with revenues of between $100,000-$250,000 (income) to serve ads promoting hiring freelance or contract help for their business.
Psychographic Segmentation
Psychographic segmentation takes customer segmentation a step further, grouping customers based on their psychological traits. Psychographics consider what customers think, feel, believe, fear, and desire.
Data about customer psychographics are typically gathered through reports, customer surveys, social listening, and marketing trend research.
These are the different types of psychographic segmentation:
- Personality: Grouping customers based on similar personality traits.
- Lifestyle: Refers to how a customer lives their daily life and how they spend their time.
- Social status: Looks into the income, social background, and where they are in their life. Example: Recent graduates, single, married, students, etc.
- Attitudes: Segments are created based on the customers’ thoughts, mental models and attitudes. This takes into consideration how the customer is raised, their cultural background, and other variables that may affect their outlook.
- Interests: Looking at customer’s activities, hobbies and preferences, and interests.
- Values: What customers believe in, opinions on certain issues, fears. Simply put, these are what the customers value in their life.
This customer segmentation model is more advanced than demographic segmentation and is used in B2B and B2C companies.
Psychographic Segmentation Example
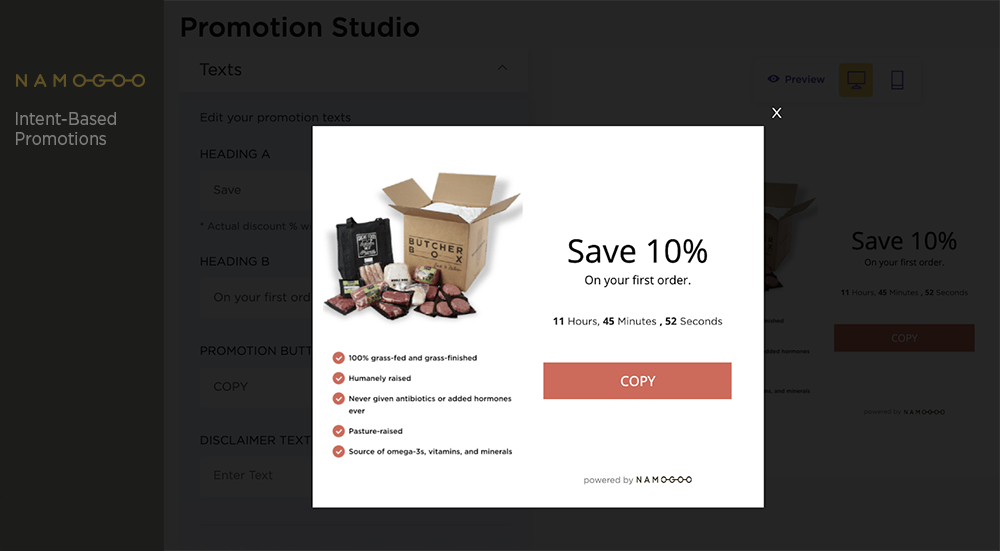
ButcherBox may create a segment based on psychographics to identify customers who value clean eating and ethically produced meat (lifestyle, values).
They could then stress those product value propositions in content, ad creative, and emails to attract their target customers, and build reminders into their onsite promotions to convert more of those visitors.
Behavioral Segmentation
Behavioral segmentation is a more modern approach to customer segmentation that meets the demands of the digital era.
This customer segmentation model groups customers on what they have actually done, based on behavioral data and analytics.
Data are more precise and gathered from clickstream data, analytics tools, and recordings. This can help marketing teams predict future actions based on past behaviors.
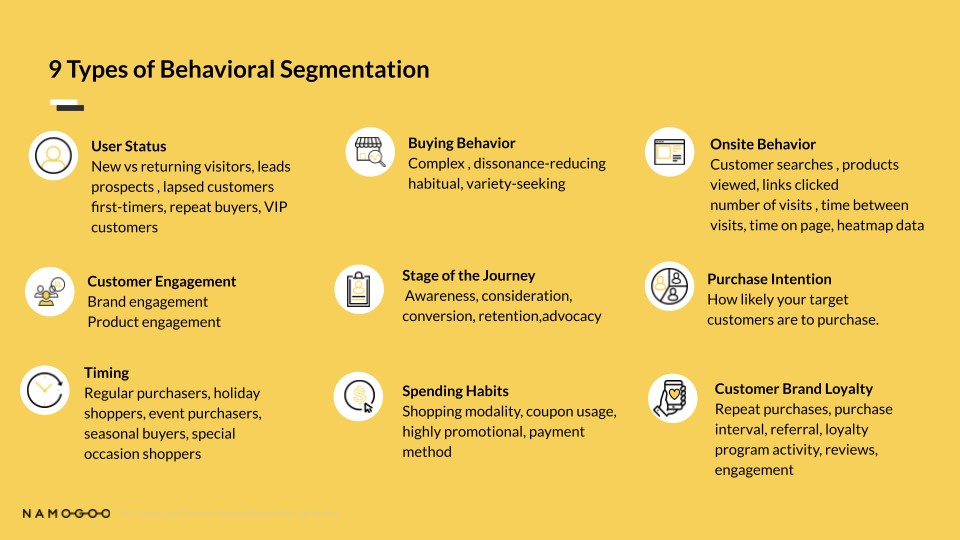
Here are the types of behavioral segmentation:
- User Status: Customers are grouped based on their current standing with a brand including new and returning visitors, leads, prospects, lapsed customers, first-time buyers, repeat customers, and VIP customers. It helps brands create a personalized offer and customer experience that can convert visitors into buyers.
- Buying Behavior: There are four patterns for buying behavior or purchasing behavior, including complex, dissonance-reducing, habitual, and variety-seeking.
- Onsite Behavior: This is the customer interaction or how they behave on your website. Some of the actions include links clicked, products viewed, time on page, pages landed on, what they searched, and heatmap data.
- Customer Engagement: This has two categories:
-
-
- Brand – Sees the capacity of how online shoppers interact with the brand, ranging from light, medium, up to heavy users.
- Product engagement – Looks at the frequency of customer’s interaction with the product.
-
- Stage of the Customer Journey: Customers are grouped based on their customer journey stage: awareness, consideration, conversion, retention or advocacy.
- Purchase Intention: Considers what the buying propensity is for each customer during each session.
- Timing: When customers buy (i.e. regular, holiday, event, seasonal, and special occasion shoppers).
- Spending Habits: How the customers spend and when they spend their money. Data used are: shopping modality (in-store or online marketplace) coupon usage, highly promotional (full-price or sale), and payment method (credit, debit, or store card).
- Customer Brand Loyalty: This behavioral segmentation is based on how loyal your customers interact and engage with your brand. It considers if a customer repeats their purchase, their purchase interval, if a customer has driven referrals, engaged in loyalty programs, leaves a review about the product and service, or engages with the brand across different platforms.
This customer segmentation model is the most advanced customer segmentation model and is used in B2B and B2C companies.
Behavioral Segmentation Example
You can use behavioral data and predictive analytics to identify users who are about to abandon their carts (onsite behavior) and deliver an incentive to keep those most likely to purchase (for example, desktop users) on the page before they abandon.
You can take this strategy to the next level by offering the promotion that is most likely to entice each customer to convert based on real-time purchase intent with Intent-Based Promotions.
Read more: 9 Advanced Behavioral Segmentation Examples to 10x Growth & Conversions
How to Develop & Convert Effective Customer Segments
Customer segmentation will only be effective if your strategy is actionable. And actionable customer segmentation is built on data.
First, you need to understand exactly what you want to achieve through customer segmentation. You’ll then select the segments that will help you achieve your objectives, before building them and targeting them with unique marketing messaging.
Finally and importantly, you’ll layer individualization into your segmentation strategy to convert, retain, and delight the customers you attracted through your segmentation efforts.
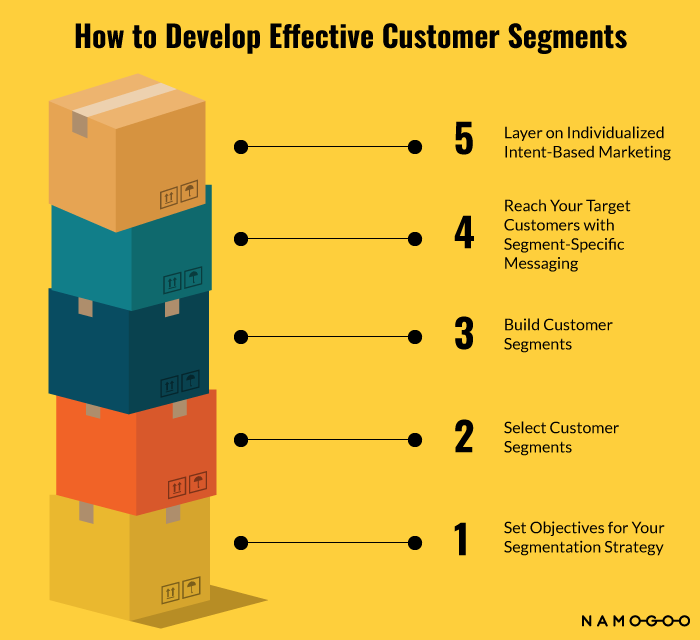
Step #1: Set Objectives for Your Customer Segmentation Strategy
The first step to building effective customer segments is to determine what your team is trying to achieve through segmentation.
Setting objectives helps you to measure the success of your segmentation strategy.
The objectives of your segmentation strategy should parallel your team’s overall OKRs or goals and encompass the desired benefits of segmentation from the list above.
For example, one of my eCommerce team’s annual OKRs may be as follows:
- Objective: Boost customer journey continuity through an improved conversion funnel
-
- Key Result #1: Increase qualified traffic by 25% through targeted, relevant content and messaging
-
- Key Result #2: Improve conversion rate by 15% via strategic email and personalized onsite offers
-
- Key Result #3: Increase repeat purchases by 10% through improved customer lifecycle management.
In this case, my objectives for customer segmentation may be to:
- Identify qualified prospects and target each group with specific marketing messaging
- Improve conversion rates through personalizing the onsite customer experience and providing the most relevant promotion to each customer segment
- Nurture new and existing customers to incentivize repurchases and retention.
Step #2: Select Your Customer Segments
You could build an infinite number of segments with the three models covered above, going as broad as everyone in a certain country (demographic) to as narrow as every new Facebook visitor abandoned their cart (behavioral).
But just because you can develop a million customer segments doesn’t mean you should. Avoid getting lost in the weeds by considering the objectives you set for your segmentation strategy.
Which segments will help you effectively meet your goals?
To provide customers with the clothing that is most relevant to them.
But for a brand like Upwork, gender is likely irrelevant and they may do better to segment based on the type of business customers are looking to hire freelancers for.
In the example above, I might choose to start with these segmentation types:
1. Identify qualified prospects and target each group with specific marketing messaging
a. Age, gender and country [demographic]
Example: Targeting 28-36-year-old women in the U.S.
b. Interests and pain points [psychographic]
Example: Beginner runners
2. Improve conversion rates through personalizing the customer experience and providing the most relevant promotion to each customer segment
a. Timing-based [behavioral]
Example: Celebrating an anniversary in the next 60 days
3. Nurture new and existing customers to incentivize repurchases and retention
a. User status and brand loyalty [behavioral]
Example: New customers who made their first purchase within the last 30 days.
Step #3: Build Your Customer Segments
After you’ve set the objectives you want to accomplish using customer segmentation, and selected the segments to help you reach them, you need to build the segments.
Customer segments are typically built in your customer relationship management (CRM) software or email service provider (ESP). You will build your segments in the same place as you store your customer contact information. For example, you might build and store your segments in HubSpot, Klaviyo, or Salesforce.
Then, other platforms (such as eCommerce platforms like Shopify, analytics platforms like HotJar, etc) feed data into your segments often through API.
Step #4: Reach Your Target Customers with Segment-Specific Messaging
Once you have your core segments built, you can begin to use them as customer acquisition engines.
Target each specific segment through developing marketing messaging, creative, and content to appeal to each through your:
- Owned media channels: Drive organic search traffic, social media shares, and lead generation through content, email, and social media marketing.
- Paid media channels: Target your segments through digital advertising platforms like Facebook and Instagram, Google, Pinterest, and LinkedIn.
Enjoy the snowball effect of customer segmentation within the algorithms of paid media and analytics platforms. The more customers in each segment, the more data is fed into the algorithm, leading the algorithm to become better at:
- Identifying high-value target customers using lookalike audiences
- Predicting customer behavior such as when they might lapse, when they might open and engage with email, etc.
Most teams stop here. Don’t be like most teams. You’ve spent time strategizing, goal-setting, and developing segments, and marketing budget targeting those segments. Now you need to convert them with the next step.
Step #4: Layer on Individualized Intent-Based Marketing
One massive limitation of customer segmentation is that it’s impossible to get as granular and specific as you’ll find that you want.
Within each segment of your customers, there are dozens (if not hundreds) of possible sub-segments – right down to individual, single-customer segments based on their customer demographic, psychographic, and behavioral data.
For example, let’s say that Abby and I are both:
- 32-year-old women living in the same city in Canada (demographic: gender, age, city, country)
- Runners (psychographic: hobby, lifestyle) training for the same half marathon (psychographic: goals)
- We are both first-time visitors to ASICS’ website (behavioral: user status) from the same Facebook ad campaign (behavioral: onsite behavior)
- In the consideration stage of the customer journey (behavioral: customer journey stage).
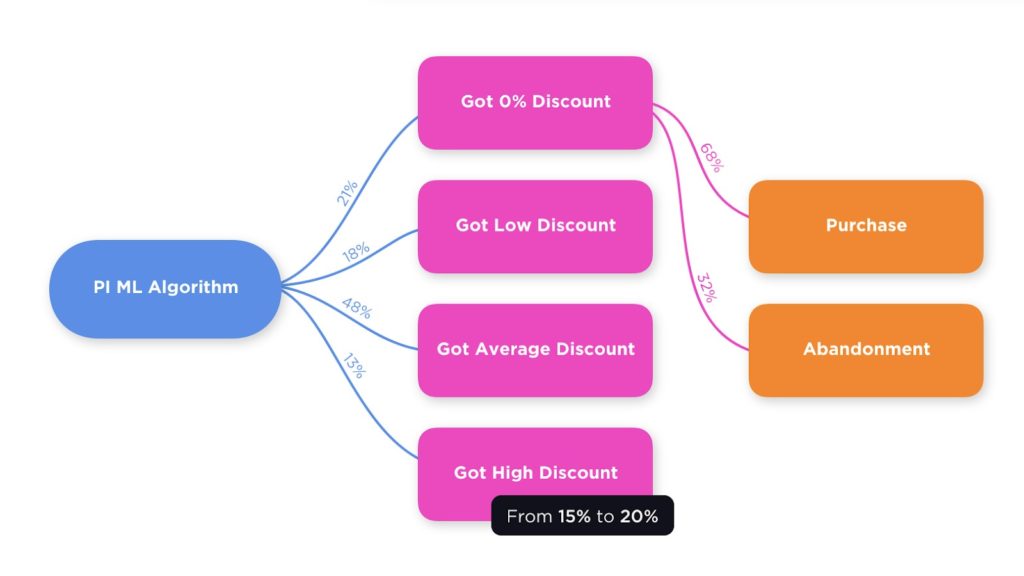
The Facebook ad targeting was clearly successful in driving both of us to ASICS’s eCommerce store. But consider what happens when we differ in purchase intention:
- My customer purchase intent is high, and my behavioral analytics suggests that I’m not that price-sensitive
- Abby’s purchase intention is somewhere between informational and transactional (falling near “medium” on a scale) and her behavioral data suggests she is more discount sensitive…
Then ASICS would be leaving valuable revenue and brand equity on the table by giving me the same onsite promotion as they presented to Abby.
I might have converted with no discount at all, and Abby may have needed a welcome offer of 15%.
This is a specific example, and it might seem unimportant, but it’s not. Every single visitor that lands on your site, no matter their customer segment, has individual behaviors and triggers.
If you set your customer segments and leave it at that, you’ll leave conversions, margin, brand equity and customer lifetime value on the table.
This is why it’s crucial that eCommerce brands layer on the revolution of customer segmentation, intent-based, 1:session AI.
Attract your customers with segmentation, and convert your customers and drive eCommerce profitability with Intent-Based personalization onsite.
Optimize the Customer Journey with Segmentation & Personalization
Customer segmentation is a cornerstone of developing a sustainable, scalable marketing strategy in eCommerce.
It enables eCommerce brands to target, attract, convert, and retain customers through specific messaging and acquisition channels.
When you add individualized real-time marketing based on behavioral, environmental, device, website and product data and predictive analytics, like with Intent-Based Promotions, you become unstoppable.




